Why IPM is the Secret Solution to Your Gardening Success
What if someone told you that the more you use most insecticides – the less they work to eliminate plant pests? Unfortunately, this is an inconvenient truth for all cultivators.
Have you ever seen mites on your plants, found the strongest chemical insecticide you could buy behind the shelf, used it with some early success – only to find that the mites ultimately come back stronger than EVER? Over time, no matter how often you spray your plants, the mites will become resistant to that insecticide, and they will not die!
What can you do? Well, there is a solution. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a practice that allows cultivators to keep pests away from plants reliably and consistently.
What is Integrated Pest Management (IPM)?
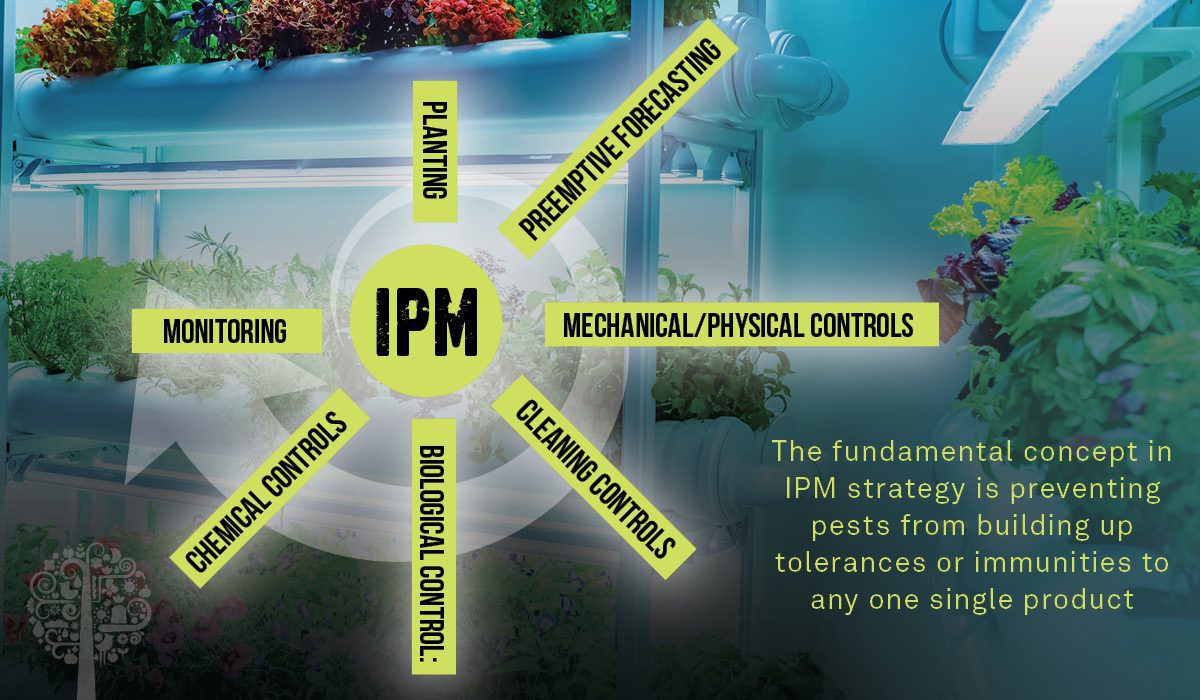
- IPM is a practice that encourages the use of several different plant protection products in a rotation schedule, which will successfully KEEP PESTS OFF YOUR PLANTS FROM SEEDLING THROUGH HARVEST.
- A good IPM strategy focuses on a variety of methods throughout your plants’ life cycles:
- Planting: Choosing a disease-resistant strain of your crop can help right from the start.
- Preemptive Forecasting: whether you are growing indoors or outdoors, monitor the climate conditions to determine if a pest outbreak might occur. For example, humidity levels are strongly correlated with mould and mildew outbreaks.
- Mechanical/Physical Controls: These controls include using the right environment, humidity, temperature, nutrition, and irrigation.
- Cleaning Controls: Quarantining new plants or clones, using clean tools and correct irrigation strategies and/or cross-contaminating your garden with outside influences.
- Biological Controls: Introducing natural predators for your pests.
- Chemical Controls: Good IPM strategies can use chemical solutions along with natural solutions. The best plans are balanced approaches that use chemical controls only as needed and rely on more naturally-based products that reduce any regulatory risk posed using synthetic chemical products.
- Monitoring: Always Be Checking your plants for pest presence signs; the simple ABC’s for IPM success!
Why implement an IPM strategy?
- Short answer: IPM works.
- IPM helps with consistent long-term pest prevention.
- Implementing and using a strong IPM strategy by rotating plant protection solutions can eliminate pest pressure. Instead of using one product with limited results, IPM practices rotate multiple products with different modes of action across the plant lifecycle.
- IPM is a sure way to eliminate pests because they cannot build up a resistance to any one product.
What is a Mode of Action?
- A mode of action is the way a particular product works to prevent and/or kill pests.
- For example, one mode of action could be trapping an insect using a sticky trap.
- Another mode of action could repel pests using certain fragrances or chemical signalling to drive pests away.
- Additionally, a mode of action could inhibit insect respiration (breathing) or cell wall structures to kill insects altogether.
- Cultivators should use different products in their rotation with varying modes of action, affecting different insect and pest biological systems. This is the key to a successful IPM strategy.
- The fundamental concept in IPM strategy is preventing pests from building up tolerances or immunities to any one single product.
How to get IPM to Work for You
Every IPM strategy is unique. Commercial cultivation facility success is dependent on a strong IPM strategy. To make an IPM plan, here are a few easy steps:
- Know your pest. Be sure you know what you are up against. Keep an eye out for most common problems in your area (disease or insect).
- Monitor your plants. Always Be Checking your plants. Be sure to keep a record of what you observe. Set a threshold.
- Have a plan. IPM is a preventative strategy. Knowing what you may need before you need it and proactively putting a plan in place is essential in creating a strong IPM strategy. The key to your system is to be sure you rotate different modes of action.
- Act! If pests start appearing, take immediate action! Use your IPM rotation as planned. You will rid pests while avoiding risking their return!
IPM; a safer, more effective method to handle your pest problems. Keep reading to learn more about how easy and effective a good IPM strategy can be for your operation.

- Colin Bell
Trending Articles Today
Similar Articles
How To Get Rid Of Aphids On Your Plants Naturally
They say observation is critical to any successful garden. Watching your plants grow will help you learn how they respond to various techniques and environmental

Why Is There Mold Growing In My Seedling Tray?
Seed starting season is upon us, and with every new planting comes a new set of problems. Got mold? Avoid it by following these tips and tricks.

Pest Prevention: The Itsy Bitsy Spider Mite
Pests are a fact of life in the garden, but there are ways to keep them out! Rich Hamilton guides us on how to prevent and treat a spider mite infestation.

